Contents
What is Workability of Concrete?
Workability of Concrete definition, the property of fresh concrete mixture, which is demonstrated by the useful internal work required to fully compact concrete without bleeding or segregation on the finished concrete surface.
Workability is one of the major physical parameters of concrete, which affects the durability and strength of the Concrete. The concrete is workable, when it is thoroughly mixed and compacted homogeneously, that is without segregation and bleeding.
Types of Workability of Concrete
1. Unworkable Concrete
Unworkable Concrete also Called as a Harsh Concrete. It is concrete with very less amount of water content. A hand mixing of this type of concrete is not so easy.
These types of concrete have high segregation of aggregates, as cement paste is not lubricated properly to stick to aggregates. In this type of concrete, it is very difficult to maintain homogeneity of concrete mix and compaction requires more efforts. Water cement ratio for this type of concrete is below 0.4.
2. Medium Workable Concrete
This type of Concrete is used in most of the construction work. This type of concrete is comparatively easy to mix, transport, pour and compact without any segregation and loss of homogeneity.
Water cement ratio of Medium workable concrete is 0.4 to 0.55. This type of Concrete is used in construction with light reinforcement (Generally, a spacing of reinforcement allows concrete to compact effectively).
3. Highly workable Concrete
This type of Concrete is relatively very easy to mix, transport, pour and compact. This type of concrete is used where effective compaction is not possible or in mass concrete. Highly workable concrete flow easily and settle down without any effort. But there are very higher chances of segregation and loss of homogeneity in this case.
Such concrete is used where heavy reinforcement is used and where the vibration of concrete is not possible. Highly workable concrete is self-compacting concrete. Water cement ratio for this type of concrete is more than 0.55.
Read Also: Top 10 Best Cement Companies In India 2021
Read Also: Difference Between Shallow Foundation and Deep Foundation
Factors affecting the workability of Concrete
1. Cement Content ratio
Additional Cement Content in Concrete affects the workability of concrete in good measures. More cement content in concrete provides flexibility and smooth concrete surface and it thoroughly fills voids between aggregates.
This also helps to reduce friction between aggregates and smooth movements between aggregates while mixing, placing and compacting of concrete.
If the fineness of the cement increases, then it will require more water for smooth workability comparatively with less fine cement.
2. Wate/ Cement Ratio or Water Content in Concrete
Water cement ratio is one of the crucial parts of the concrete, which influence the workability of the concrete. However, the water-cement ratio of 0.45 to 0.6 is used for better workability without even using any additional Admixture to Concrete.
Higher the water-cement ratio, the higher the water content per volume of concrete and Concrete will be more workable. The higher water-cement ratio is normally used for manual concrete mixing work for better workability.
3. Mix Proportion of Concrete
Mix proportion of the Concrete explains us the ratio of coarse aggregates and fine aggregates with respect to Cement Content. This is also called an aggregate cement ratio of concrete. The more cement is used, the concrete becomes richer and aggregates will get proper lubrication for smooth mobility or smooth flow of aggregates.
If the less cement content in concrete with respect to aggregates, then there will be less pest available for aggregates and smooth mobility of aggregates is restrained.
4. Size of Aggregates
A surface area of aggregates relies upon the size of aggregates. For the unit volume of aggregates with large size, the surface area of less contrasted with the same volume of aggregates with Small size.
When the surface area of aggregates increases, then the requirement of the cement content also increases to cover the entire surface of aggregates with cement paste. Moreover, this requires the use of more water to lubricate each aggregate.
However, the lower size of aggregates with the same water content is less workable than the large size of aggregates.
5. Shape of aggregates
The Shape of aggregates directly effects on the workability of concrete. It is very understandable that rounded shape aggregates are very easy to mix than elongated, angular and flaky aggregates, due to less frictional resistance.
Other than this, the rounded aggregates have a less surfaced area compared to elongated or irregular shaped aggregates. So, this requires very less water content for the same workability. Therefore, the river sand is preferred for concrete as they are in round shape.
6. Grading of aggregates
Well-Graded aggregates have a major effect on the workability of concrete. Well-graded aggregates help in reducing the voids in the given volume of aggregates.
If the grading of aggregates is good then there will be less chance of voids in between. Hence, it improves the workability of concrete.
7. The surface texture of aggregates
A surface texture, such as rough surface and smooth surface of aggregates affects the workability of concrete in the same way as the shape of aggregates.
Rough textured surface area aggregates have a more surface area than the aggregates of the same volume with a smooth textured surface. Though, Concrete with smooth surface texture is more workable than rough-textured surface aggregates.
8. Use of Admixture in Concrete
There are many different types of admixture used in construction to enhance the properties of concrete. There are few workability enhancers, such as plasticizer and superplasticizers, which increases the workability of the concrete even with less water-cement ratio (resulting, delay in initial setting time). Admixture reduces the quantity of water required for the same value of slump.
9. Use of Supplementary Cementitious Materials.
Supplementary Cementitious Materials are those materials, which are used with cement to modify properties of concrete. These materials are as follows, Fly ash, fibers, Silica fume, slag cement.
The uses of Fly ash are to improve the workability of the concrete by reducing water content required for the same slump value.
Read Also: What is Shallow Foundation | Types of Shallow Foundation
The use of synthetic fibers in concrete, it reduces workability of concrete as it makes the movement of aggregates harder by reducing the lubricating effects of cement paste in concrete.
The Silica fume is used in concrete to reduce and increase the workability of concrete based on its quantity. The silica fume can improve the workability of concrete when used at low replacement rates, but it can reduce workability when it added at a higher replacement rate.
The use of slag cement improves the workability of concrete when its effects depend on the characteristics of the concrete mixture in which it is used.
Types of Workability test of Concrete.
List of Concrete workability test
- Slump Test
- Compaction test
- Vee-Bee sensitometer test
1. Slump Test
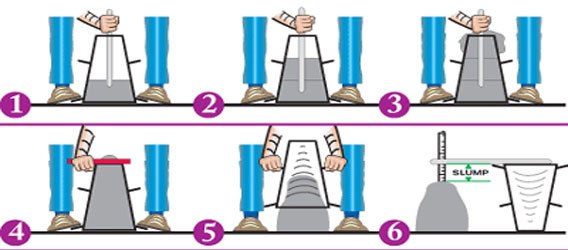
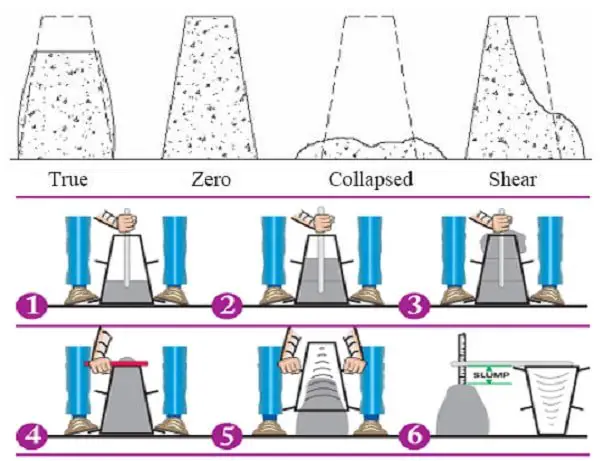
A concrete slump test is carried out with a mould called slump cone. Slump Cone’s top diameter is 10 cm, bottom Dia is 20 CM and height is 30 cm.
Process of Slump Test
- Place the slump mould on the smooth plain surface.
- Mix the dry ingredients of the concrete properly until a uniform color is formed, then add the required quantity of water.
- Pour the mixed concrete in mould about 1/4th of its height.
- Start compacting concrete with compacting rod 25 times with the help of tamping rod, uniformly all over the area.
- Again, pour concrete in mould half of its height, then compact again.
- Pour the concrete up to its 3/4th height and compact, then up to its top. Compact each layer uniformly 25times with tamping rod.
- Level the top surface of the mould with a trowel, so that mould is filled to its top.
- Now remove the mould immediately, ensuring its movement in an upward direction.
- Then Concrete begins to settle, when the settlement of concrete stops, measure the subsidence of the concrete in MM which is the required slump of concrete.
Recommended Values of Concrete Slump test for Various purpose.
| Sr No. | Types of Concrete | Required Slump |
| 1. | Concrete for Road Construction | 20 MM to 40 MM |
| 2. | Concrete for tops of curbs, parapet, slab, walls, and Column | 40 MM to 50MM |
| 3. | Concrete for Canal Lining | 70 MM to 80 MM |
| 4. | Normal RCC Work. | 80 MM to 150 MM |
| 5. | Mass Concrete | 20 MM to 50 MM |
| 6. | Concrete to be Vibrated | 10 MM to 25 MM |
Read Also: What is Compressive Test of Concrete | Cube Test and Procedure
References: ACI 238.1R-08 – Report on Measurements of Workability and Rheology of Fresh Concrete
Workability of Concrete (Video Tutorial)
Workability of Concrete definition, the property of fresh concrete mixture, which is demonstrated by the useful internal work required to fully compact concrete without bleeding or segregation on the finished concrete surface.
1. Slump Test
2. Compaction test
2. Vee-Bee sensitometer test
Read Also: What is Deep Foundation | Type of Deep Foundation
Read Also: What is Formwork in Construction | Types of Formwork


Very interesting post, Thanks for sharing such useful information here, I must visit your site for more in the future. I have shared some data on
Workability of Concrete and Factors Affecting Workability you may like to look into
Thanks for sharing this post. It is really helpful to understand
What is Workability of concrete
great