Contents
What is Surveying
Surveying is the art and science of determining the relative position of points on, above or beneath the surface of the earth by means of direct or indirect measurement of distance direction or elevation, The Application of Surveying required skills as well as the knowledge of mathematics, physics and to some extent astronomy.
It also includes the art of establishing points by predetermined angular or linear measurement to the site location
The mensuration taken may be vertically or horizontally. In the case of horizontal measurement, the paper on which they are drawn is known as maps of our plans. In the case of vertical measurement. they called section or elevation
Generally, before Start of any Engineering works a typographical plan or map with horizontal and vertical measurements are required, surveying also includes establishing points by predetermined linear and angular measurements
Surveying is the procedure of analyzing and recording the features of a land area cent to help design a plan or map for construction. Surveyor works with the elements of geometry trigonometry decoration analysis physics engineering metrology programming language, and the law they used equipment like total stations robotic total station GPS receivers retroreflectors, 3d scanners radios handheld tablet digital levels, drones GIS and Surveying software among all of the equipment total station is the current preferred Surveying equipment in the industry.
Some more about Surveying
- The surveying of art or map structure has been practiced from the very primitive time.
- The earliest surveys Known were performed only for the purpose of establishing the boundaries of lands, but their Application has become increasingly important as the time has progressed
- Now, a day for the purpose of designing any engineering projects such as road’s, railways, canals water supply or Sanitary scheme, etc
- An engineer would require to study as the very first items, the features of the Earth surface in which the project is to be located and prepare a map of that area.
- The success of any engineering projects is based upon the accurate and complete survey work
- A civil engineer so, must be completely familiar with the principal and exercises of surveying.
Leveling:- it is the branch of surveying, which is used in determining the relative elevation of any object with respect to datum line and to establish the point at a given elevation or at different elevation with respect to a given or assumed datum
Why surveying is important or Used
- Surveying is used in preparing a topographical map. which represents hills, valleys, villages, town’s forest, etc.
- It is also used in preparing engineering maps which shows the details of engineering works such as road’s, railways, etc
- It is used in preparing a cadastral map. which shows the boundary of fields houses and other properties.
- It is used in preparing the military map which show’s the road’s, railway and communication of different parts of country
- It is used in preparing a contour map to determine the capacity of a reservoir or also helps to find the best possible transportation routes
- It is used in preparing a “geological map” showing area natural resources.
- Also used in preparing an archaeological map
Types of Surveying
There are two types of Surveying
1. Plane Survey
- The surveying where the effect of the curvature of the Earth is neglected consuming the earth surfaces to be plane is called plane surveys.
- The degree of precision acquired in this type of surveying is relatively less.
- Generally, an area less than 260 sq km is treated as a plane.
- The controlling factors should be the degree of accuracy required rather than the area of the Survey
- The scope and use of plane surveying are wide as it is employed in the majority of surveys conducted for the purpose of engineering works.
2. Geodetic or Trigonometrical Survey

- Those surveys where the curvature of the earth is taken into account are called geodetic SurveyThese are also known as the Trigonometrical survey as they involve the knowledge of Trignometry during different operations.
- As the Survey distend over a huge area or the degree of precision required is great, the curvature of earth can’t be neglected
- Geodetic Surveying is generally adopted to locate the wide distance control.point for different surveys to be conducted in between these points
- It requires the use of the Very refined instrument as well as methods of observation and adjustment
- It is operated only via government agencies such as in India.
- It is conducted by the great Trigbometrical survey (GTS) department of India.
What is measurement and Units of Surveying
- In Surveying, a surveyor has to generally deal with a linear and angular measurement taken in the horizontal plane are Known as “horizontal distance” whereas those taken in the vertical plane are called “vertical Distance”
- Similarly, the angular measurements are horizontal angles, and vertical angles, when taken in horizontal and, vertices plan respectively.
- 1 sq .in = 64516 sq km , 1 inch = 2.54cm1 sq ft = 0.0929 sq .m , 1 foot = 0.3048m
- 1 sq nule = 2.59 sq m , 1 mile = 1.6093 km
- 1 acre = 0.4047 hectare
Linear measurements
There are two main system of measurement.
- MKS ( metric, kilograms, second) or metric system
- FPS ( Food , pound, second) or British system
- The unit of length is a meter in the MKS system and a foot in the F.P.S system.
- Previously, Indian followed the FPS system of measurement but from 1956 according to the weigh and measurement act, the metric system has become the only recognized system in India.
Angular Measurements
A radian is the units of plane angle and is equal to the angle sustained at the centre of a circle by an arc equal in length to its radius.
- π radian = 2 right angles
- 1 right angle = 100 grades or 90 degrees A degree is the basis Unit of the angle used in India
- 1 degree (°) = 60 minutes’
- 1 minutes (‘) = 60 second
The instrument used in Surveying
The instrument commonly used for taking surveying measurement may be divided into the following main classes:-
- The instrument used for ranging and laying out survey lines such as ranging rod, line ranger cross-staff, optical square, etc.
- an instrument used for direct measurement of length such as Chain, tape, Steel band, etc
- The instrument used for measurement of length indirectly such as tacheometer substance bar
- Instrument used for determining the direction of line such as prismatic compass, box
- sexy ant, theodolite, etc.
- The instrument used for measuring slopes and height such as clinometer level etc
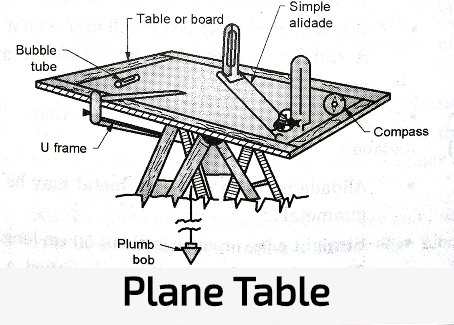
- Instrument Used for surveying and plotting simultaneously such as a plane table.
- Instrument Used for surveying Bhai photographic means such as phototheodolite.
Basic principles of Surveying
The following two basic principles of surveying should be kept in view while determining the relative position of points on the surface of the earth:-
- Determining a suitable method for locating a point
- Working from whole to the part
Determining a suitable method for locating a point
it is always practiceable to select two points in the field and to measure the distance between them.
These can be represented on pasteboard by two points. Placed in a convenient position
From these initial point also known as reference. Point Other can be located by two suitable measurement in the field and drawn in their relative position on the sheet.
Points so obtained serve in turn to fix the position of others. Working from whole to the part
In Surveying and area it is essential to establish first of all a system of control point with great precision
Minor command points can then be instituted by less appropriate method and the details can be located subsequently by the method of triangulation or cross between the control points.
That way the minor errors are automatically controlled or localised and don’t accumulate.
On the other side, if we work from part to the whole, the minor errors are magnified and become uncontrollable at the end.
A general classification of surveys
Surveys may be classified into the following different ways:- According to the instrument used such as
- Chain survey
- Plain table survey
- Theodolite Survey
According to the objective of survey such as
- My survey to explore mineral wealth as gold, copper, coal, etc. Within the earth’s crust.
- Geological survey to determine apart strata in the earth’s crust.
- Archaeological survey to mark customs or residues of the past
- Military Survey to determine the signal of strategic importance
According to the method employ such as
- Triangulation Survey
- Traverse Survey
According to the work of place such as
- Land survey for an object on the earth surface
- Hydro graphical or marine survey for objects underwater.
- An aerial survey by Aeroplane in air.
A land survey can be further subdivided into the following classes
- Typographical survey:- it is used for determining the natural features of the country such as lakes, rivers, hills, woods, etc and also the artificial object such as canals, railways, roads, Town, and village, etc.
- Cadastral Survey:- this is usually plotted to a larger scale than typographical survey additional details such as boundaries of field, houses, and other properties are determined
- City survey:- this is performed in connection with town planning schemes such as drainage water supply etc and laying out plots, roads, streets, etc.
- Engineering Survey:– This is carried out for determining the feasibility of any engineering project and collections of field data as required for the design etc.
Work of Surveyor
The work of a surveyor can be divided into the following three parts.
- Fieldwork
- Office work
- Care and adjustment of instruments
Field work
It consists in taking measurement for details, recording field notes and setting out of work.
Office work
It consists of Ready for preparing maps, plans and part from the data collected in the field and also calculating area volumes or designing the different structures.
Care and adjustment of instrument
The Surveyor must be thoroughly familiar with the instrument which he will be called open to using.
He must also know the method of testing and adjusting the instrument.
Delicate and very costly instrument such as theodolite a level etc must be handled with great care and accuracy.
Even a minor injury is liable to make them out of order and the same can only be set to original position by costly and time-consuming repairs.
AAC blocks aluminium formwork Bar Bending Schedule BBS Bleeding in concrete block work Brick masonry brick work Cast-in-situ cement clay bricks compaction test Compressive strength cracks cube mould cube test Deep Foundation Drilled Caissons guest bedroom size kitchen size lift service light weight block living room maintenance non-structural cracks pestcontorl Pier Foundation Pile Foundation plaster work plywood formwork Post-tensioning record sheet room sizes Segregation of Concrete services shallow foundation shrinkage cracks Slump test steel formwork structural cracks timber formwork trey trowel Vee-bee consistometer What is Deep Foundation?

